Primitive Type - Empty Volume
Introduction
Shape Primitives are ray traced using a distance estimation method (a smarter ray march).
- Estimators
We have several built-in estimators:
Sphere
Cube
Cylinder
Cone
Torus
Plane
Empty Volume
An empty volume can be used to create realtime booleans in Layout.
Inigo Quilez explains the principle here and suggests an empty volume providing the distance estimator through nodes.
As LightWave is rendering this shape, each surface point can be read using the input Object Position. We translate that into its distance from the center of the volume using a Vector Length Node and then by adjusting this value with other things (i.e., maths, 3D procedural textures, etc.) we can then attach it to drive the Displacement value for the empty volume.
In LightWave, the functions are provided by adding a Null and setting it to Shape > Empty Volume. The displacement is performed by editing the object's surface. The resulting object is called a Signed Distance Function or SDF.
To make use of the presets attached here, download to disk and in the Surface Editor go to the Preset... dropdown and choose Load from Disk... - this will replace your existing surface. Once loaded you can save the surface as your own preset. The Capsule preset will require that you supply nulls for End A and End B. Without them, it will just look like a stripy ball.
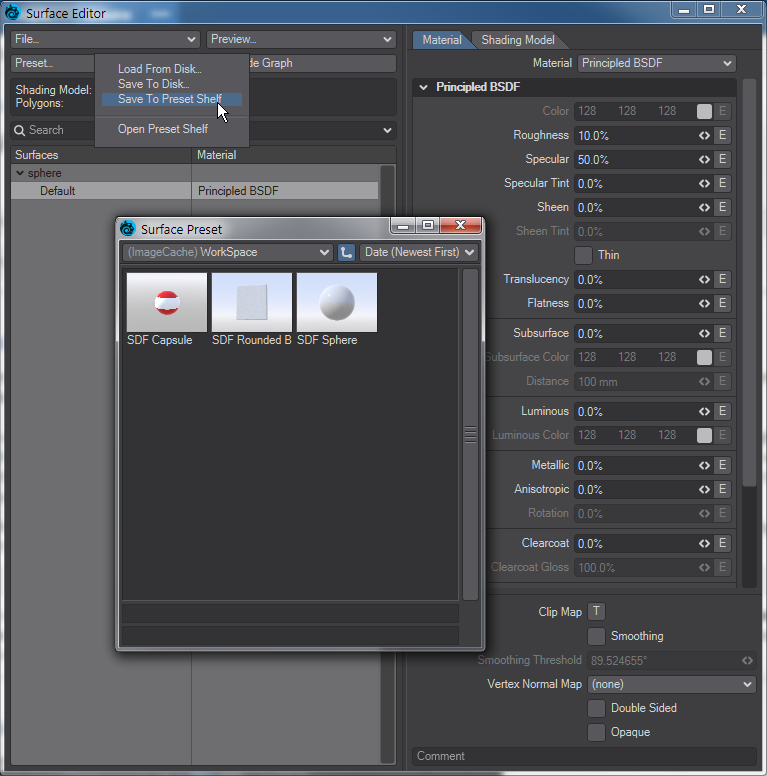
Distance functions drive the iso-surface boundary finding. A simple node showing the sphere primitive shape in an empty volume.
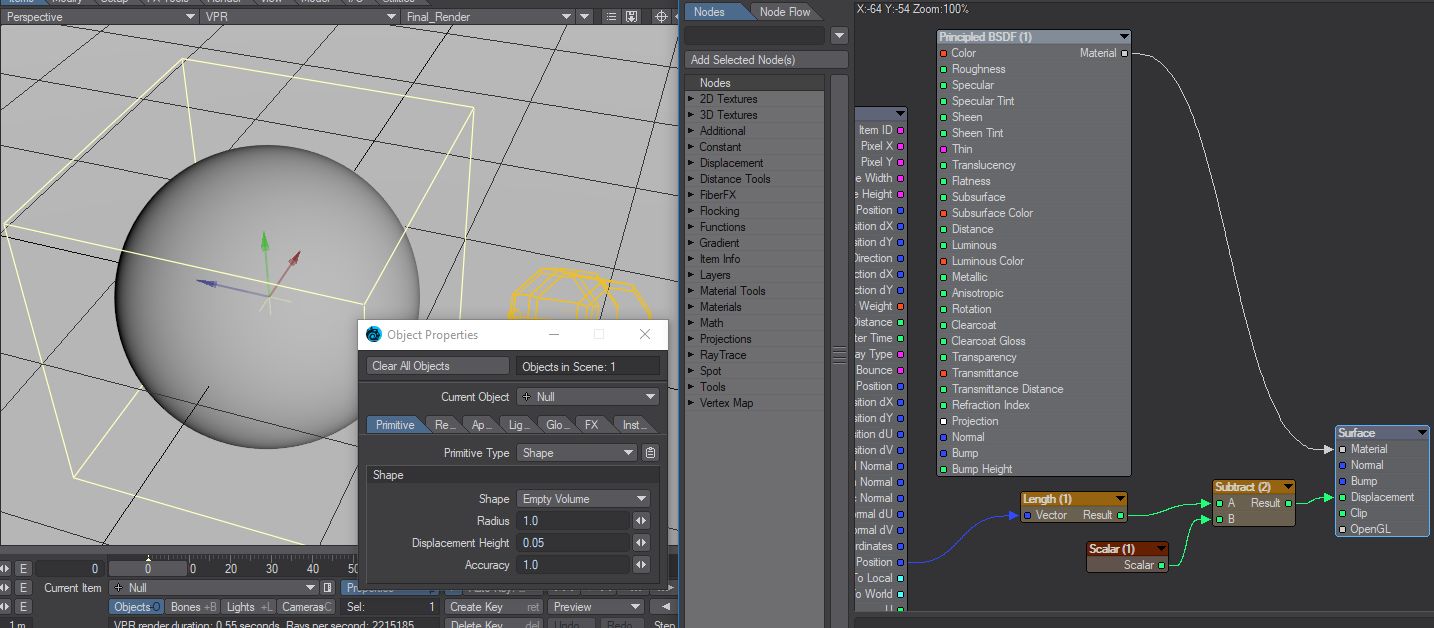
A rounded box derived from http://iquilezles.org/www/articles/distfunctions/distfunctions.htm
Distance Tools
Distance Tools menu heading contains nodes to create or modify distance functions.
Capsule
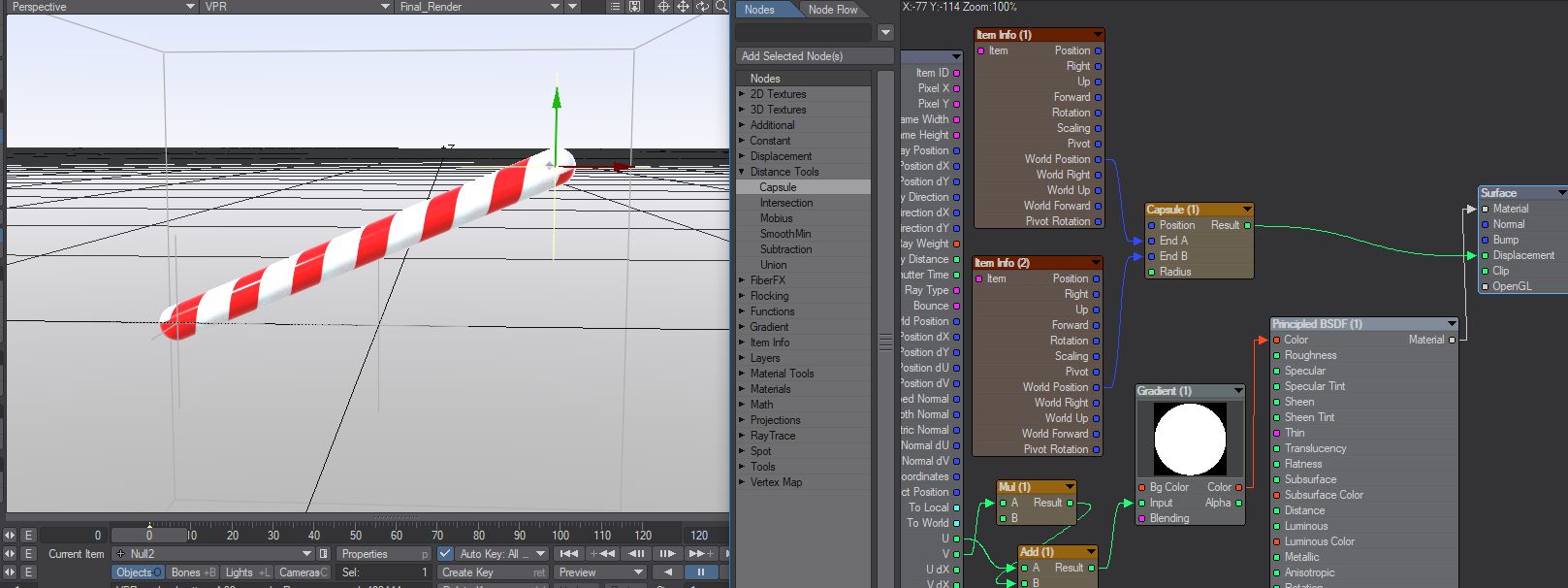
The capsule node relies on positional information based on the End A and End B inputs, or two items (nulls were made for the preset) to form each end of the capsule. The capsule inputs determine:
Position - the location of the capsule shape. Usually the object itself, however, this can be driven by nodes
End A - One end of the capsule shape
End B - Opposite end of the capsule shape
Radius - the radius of the capsule shape
Setting both the end values to 0 will produce a spherical shape.
The attached surface preset available here relies on positional information for two items (nulls were made for this) to form each end of the capsule. The first input is taken from the Input node's World Position, and the Radius is based on a Scalar constant. The attached surface preset merely renames the inputs to make them easier to understand.
Mobius
A twisted set of a single ring. The inputs determine:
Radius - The overall size of the ring set
Cylinder Radius - The radius of the cylinder that is being twisted
Group Radius - How tightly packed the ring is
Order - How many apparent rings are being twisted together
Twist - The spiraling of each apparent ring
Coil - The spiraling of the total rings
Shape CSG
Takes the Result from two SDF shapes and combines them in the fashion that should be familiar by now -
Union - Combines the two shapes
Intersection - Only leaves the parts of the two shapes that overlap
Subtraction - Removes Shape A from Shape B
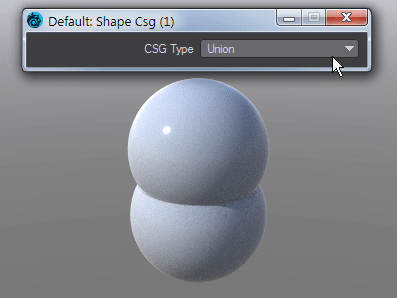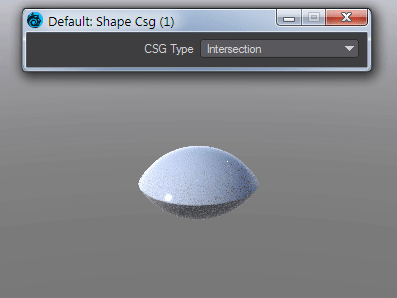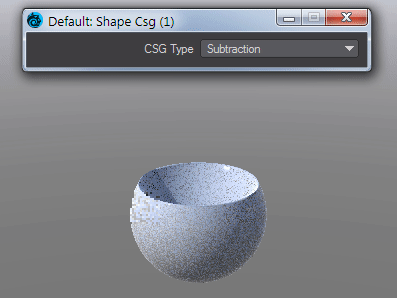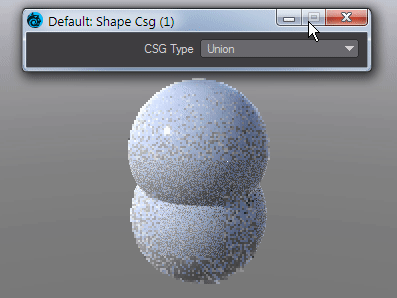

SmoothMin
Will blend between the Results from two SDF shapes with a user-definable radius.
Additional Nodes
You can use a Vector Mod (ulo) for repetition. The initial Empty Volume radius determines how many shapes will fill it. The Vector Mod can be left at 1.0, 1.0, 1.0 and the Scalar will determine the size of the individual shapes
A texture distortion of the above distance field.


