Flow: Unified Physics - Preferences
warning
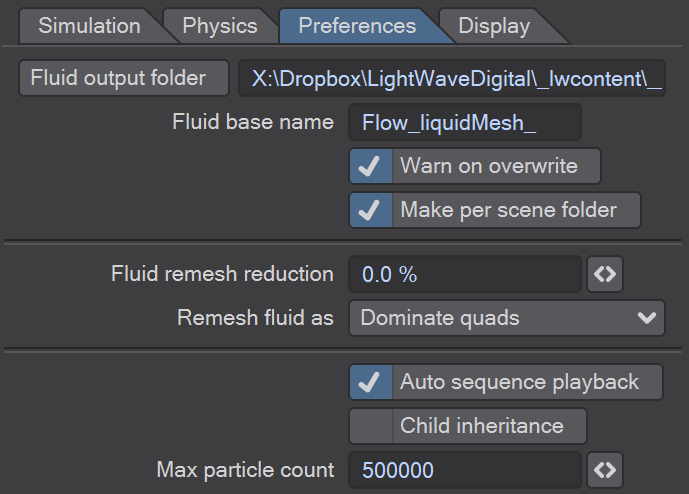
Ensure that the 'Fluid output folder' is set appropriately.
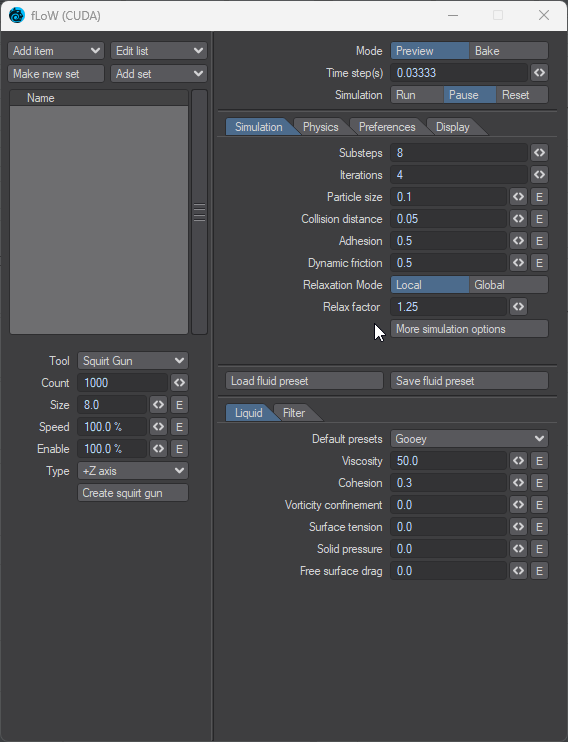
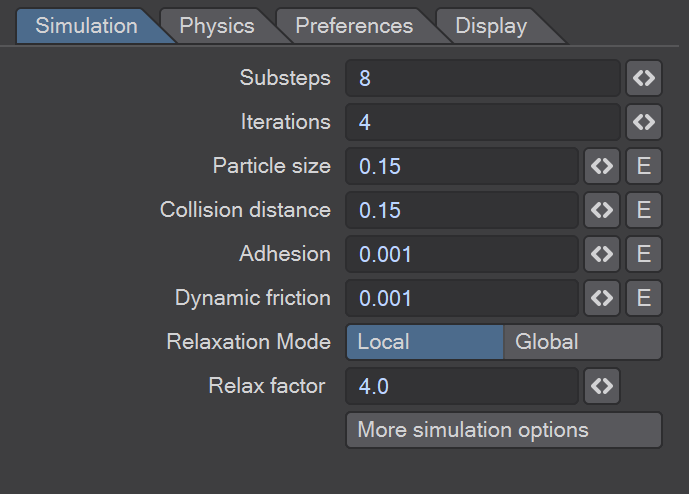
Substeps - The number of substeps (i.e. the frame rate is divided by the number of substeps to determine the number of simulation calculations done per frame) per frame where the simulation is calculation
Iterations - The number of iterations calculated for each substep.
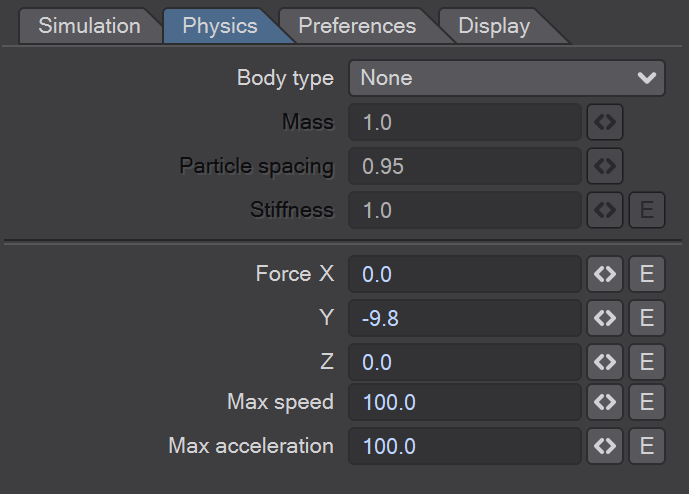
Particle size - Sets the size of the LW Flow particles
Collision distance - Distance between particles for collision detection
Adhesion - How particles 'stick' to each other
Dynamic friction - When particles collide do they steal energy from each other
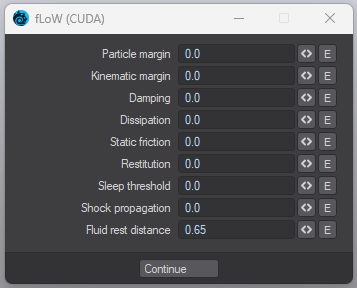
Relaxation mode - There are two options. Either Local which means the simulation is relaxed at a Local coordinate level, or Global which considers world coordinates. Choosing world coordinates will result in a longer relaxation time.
Relax Factor - The Relaxation factor is the time it takes for a particle to speed up from one velocity to another.
More simulation options - see below.